SIM-related attacks are no longer rare — they’re becoming a serious global problem affecting both individuals and businesses. From everyday users to high-profile executives, anyone with a mobile phone is a potential target. One of the most dangerous forms of this threat is called SIM jacking.
In a SIM jacking attack, criminals hijack your SIM card, taking control of your phone number. This allows them to intercept your calls, read your text messages, and capture sensitive one-time passwords (OTPs) used to log in to bank accounts, email, and social media. Once they have access, identity theft and financial loss can happen in minutes.
The risk is greater today because so many services still depend on SMS-based authentication. That’s why solutions like encrypted SIMs are gaining attention — they add an extra layer of defense, making it much harder for attackers to exploit your mobile identity.
What is SIM Jacking?
SIM jacking is the unauthorized takeover of your SIM card — the tiny chip inside your phone that holds your mobile identity. Also called SIM swapping or SIM hijacking, this attack tricks your mobile carrier into transferring your phone number onto a SIM card controlled by criminals.
The process usually starts with social engineering. Attackers impersonate you, contact your carrier, and claim that you’ve lost your phone or need a replacement SIM. Once the carrier processes the request, your legitimate SIM goes dead — and the attacker’s SIM becomes active with your number.
From that moment, they can receive your calls and texts, including sensitive one-time passwords (OTPs) used for banking, email, and social media logins. In effect, they bypass many of the safeguards people rely on every day.
High-profile cases highlight the damage: U.S. investors and crypto holders have lost millions through SIM jacking attacks, and even Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey’s account was once hijacked this way.
How SIM Jacking Works
SIM jacking isn’t a complex hack — it’s usually a mix of deception and weak carrier processes. Here’s how it typically unfolds:
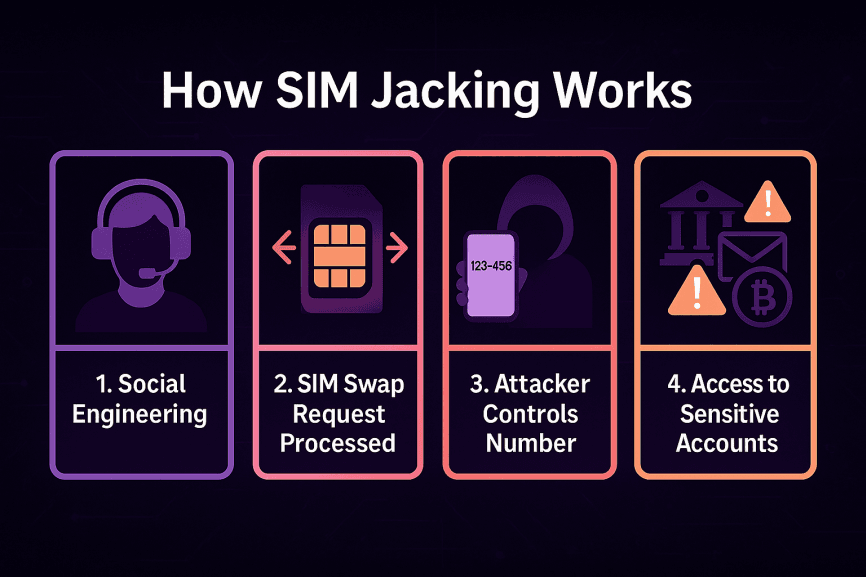
Step 1: Social engineering
The attacker gathers personal information about you — name, address, date of birth, maybe even answers to common security questions. They contact your mobile operator while pretending to be you, claiming their phone was lost or stolen.
Step 2: SIM swap request processed
If the carrier is convinced, they authorize a SIM swap and activate a new SIM card under your number.
Step 3: Attacker takes control
Your original SIM card immediately loses service. The attacker’s SIM now receives all of your calls and text messages.
Step 4: Account access
With your phone number in hand, criminals intercept SMS-based one-time passwords (OTPs) used to reset passwords or approve transactions. This gives them a direct path into bank accounts, crypto wallets, email, and social media.
Beyond social engineering, more advanced methods exist — for example, SIMjacker malware can exploit weaknesses in SIM cards to take control remotely.
This is why SMS-based two-factor authentication (2FA) is risky. While better than no security, it depends on the integrity of your SIM. If that SIM is hijacked, your second layer of protection collapses instantly.
Common Signs You’re a Victim

One of the scariest parts of SIM jacking is that it often happens without warning. Still, there are a few red flags that can alert you to trouble:
Sudden loss of mobile signal or service while your friends’ phones work fine.
Inability to make or receive calls or texts, even in strong coverage areas.
Unusual account activity, such as unexpected password reset emails, login alerts, or messages from your bank.
Carrier notifications about a SIM change or number transfer that you didn’t request.
If you notice more than one of these signs, treat it as an emergency. Contact your carrier immediately and check your most important accounts before attackers can lock you out completely.
Real-World Impact of SIM Jacking
The consequences of SIM jacking can be devastating, both personally and professionally.
For individuals, the most immediate risk is financial theft. Once criminals control your SIM, they can intercept SMS-based banking codes and drain checking accounts or crypto wallets within minutes. High-profile cases have seen victims lose hundreds of thousands of dollars through fraudulent transfers.
Another major consequence is identity theft. Attackers often hijack email and social media accounts using password resets, then impersonate victims to scam friends, spread misinformation, or further exploit sensitive data.
The risk doesn’t stop at individuals. Executives, journalists, and activists are prime targets because a compromised SIM can expose confidential communications, intellectual property, or even sources. This makes SIM jacking not just a personal threat, but a serious business and national security risk.
In short, SIM jacking affects more than just your phone. It has the power to compromise finances, reputations, and entire organizations — making prevention critical at every level.
How to Protect Yourself from SIM Jacking
The good news is that while SIM jacking is dangerous, there are clear steps you can take to reduce your risk. Prevention requires a mix of stronger carrier controls, smarter authentication methods, and everyday awareness.
1. Strengthen your carrier account
Most mobile providers allow you to set up a PIN or password on your account. This extra verification makes it harder for attackers to impersonate you when requesting a SIM swap. Call your carrier and enable this feature if it isn’t already active.
2. Limit personal information exposure
Criminals often use data from social media or leaked databases to answer security questions. Avoid oversharing your birthday, address, or mother’s maiden name online — details like these are often enough to pass a carrier’s identity check.
3. Switch to app-based authentication
Instead of relying on SMS codes, use authentication apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, or Microsoft Authenticator. These generate codes locally on your device, making them immune to SIM swap attacks.
4. Keep an eye on your accounts
Set up alerts on your email, bank, and social media accounts for logins or password resets. Acting quickly can make the difference between a scare and a major financial loss.
5. Watch out for phishing attempts
Many SIM jack attempts begin with phishing emails or texts designed to steal personal details. Be cautious about clicking links or sharing information, especially when a message pressures you to “act fast.”
By following these steps, you significantly reduce your vulnerability — and with solutions like encrypted SIMs, you can push your defenses even further.
How Encrypted SIMs Help Against SIM Jacking
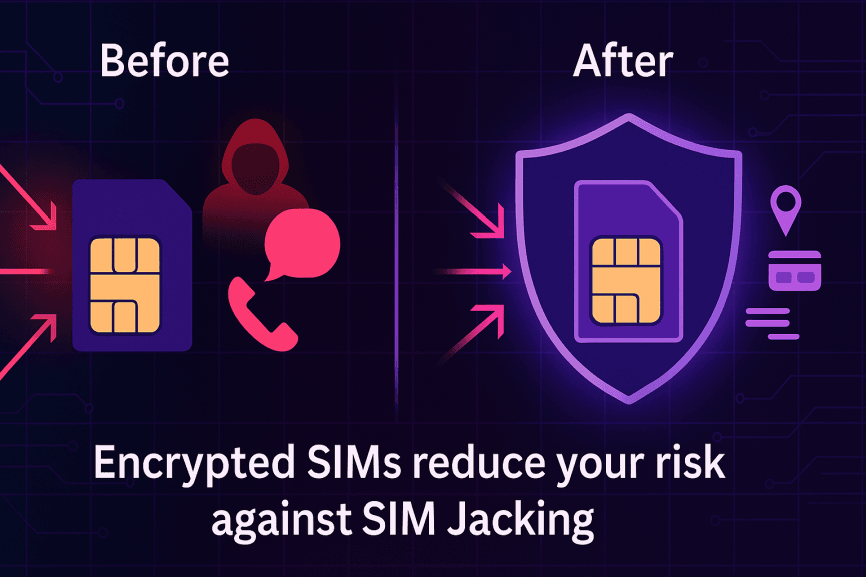
Traditional SIM cards weren’t designed with today’s advanced threats in mind. That’s where encrypted SIMs come in — a smarter, more secure alternative for anyone serious about protecting their communications. With GhostSims, you get an advanced security layer that shields not just your calls and SMS, but also your data traffic and digital identity.
Unlike standard SIMs, encrypted SIMs are built to defend against IMSI catchers — devices that criminals (or even surveillance actors) use to intercept and track your mobile activity. By encrypting your communications, they make it far harder for attackers to capture your messages or impersonate your number.
Another key advantage is metadata protection. Even if a SIM swap attempt succeeds, encrypted SIMs help obscure sensitive details like your location, call logs, and who you’ve been in contact with. This makes large-scale surveillance or targeted exploitation significantly less effective.
It’s important to be realistic: no technology can guarantee 100% protection. However, encrypted SIMs dramatically reduce the attack surface, making SIM jacking and related exploits far less likely to succeed.
For individuals, this means stronger protection against identity theft and financial fraud. For businesses, it means safeguarding executives, staff, and sensitive corporate data. Choosing a provider like GhostSims isn’t just about privacy — it’s about resilience against the fastest-growing mobile threats today.
Final Thoughts
SIM jacking is one of the fastest-growing cyber threats, and its impact can be devastating — from drained bank accounts to stolen identities and compromised business data. Protecting yourself requires more than just awareness; it demands a proactive mix of good security habits and stronger tools.
While steps like carrier PINs, app-based authentication, and vigilance against phishing are essential, they’re not always enough. That’s where encrypted SIMs come in. By shielding your calls, messages, and data from interception, they provide a powerful defense against SIM-based attacks.
If you take your privacy and security seriously, it’s time to go beyond the basics. Discover how an encrypted SIM can safeguard your communications today.
FAQs
Is SIM jacking the same as SIM swapping?
Yes — the terms are often used interchangeably. Both describe a situation where criminals trick your mobile provider into transferring your phone number to a SIM card they control, giving them access to your calls, texts, and accounts.
Can encrypted SIMs completely prevent SIM jacking?
No solution can offer 100% protection, but encrypted SIMs significantly reduce the risks. They defend against IMSI catchers, hide sensitive metadata, and make it much harder for attackers to intercept or exploit your communications, even if a SIM swap attempt occurs.
What should I do if I suspect my SIM was hijacked?
Act immediately. Contact your carrier to regain control of your number, change passwords on key accounts, and alert your bank or financial services. The faster you respond, the more damage you can prevent.
Is SIM jacking common in my country?
SIM jacking has become a global problem. It’s especially common in regions where mobile providers have weaker verification processes, but high-profile cases have occurred everywhere — from the U.S. and Europe to Asia and beyond. If your country relies heavily on SMS-based authentication, you’re at risk.
Ready to Protect Your Privacy?
Get military-grade encrypted SIM cards with IMSI masking, end-to-end encryption, and true no-log privacy. Start protecting your communications today.
Related Articles

eSIM vs Physical SIM: Which Is More Private in 2026? (Reality Check)

SS7 & Diameter Attacks Explained: How Telecom Networks Leak Your Location and Calls


